Understanding Data and Concept Drift
...The Most Important Interview Question!
No model works forever.
YES, it degrades over time!
Machine learning models are trained with historical data.
But when deployed in the real-world, they encounter live data that constantly evolves.
As the environment changes, models can become outdated and lose accuracy over time—a phenomenon called model drift.
So, let’s dive deeper into why this happens and how you can prevent model decay.
⏸️ Quick Pause: If you’re new here, I’d highly appreciate if you subscribe to receive bi-weekly data tips and insights — directly into your inbox. 👇🏻
How Your Predictions Can FAIL?
Imagine you’re a data scientist working on cab fare prediction model.
Your goal is to ensure that predicted fares closely match real-world pricing.
Your model likely relies on input features such as:
Distance of the ride,
Time of day (peak vs. non-peak),
Traffic conditions.
Weather conditions, etc.
Everything works fine—until one day, your product manager rushes in with a drastic issue: fares are way off!
Despite careful training and validation, the model’s accuracy has plummeted.
What’s Going Wrong?
After ruling out any data quality issues, two usual suspects emerge: data drift and concept drift—two critical challenges in production ML system.
So, it’s important to understand the difference between them because they require different approaches to detect and fix.
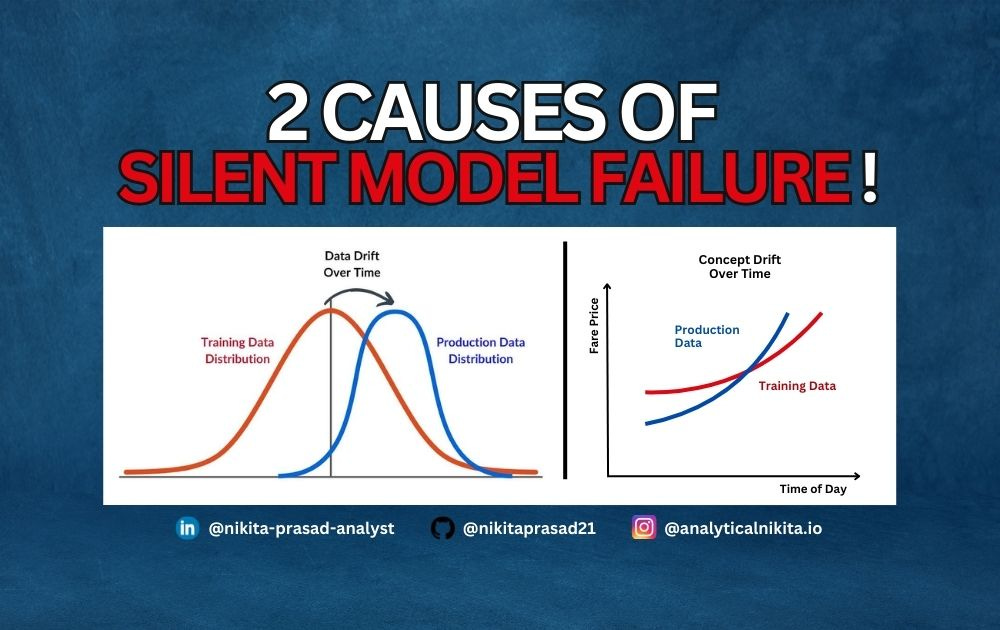
What is Data Drift?
Data drift happens when the statistical distribution of input data changes.
And this shift leads to unreliable predictions because the model encounters unfamiliar patterns.
Example:
Your cab fare model was trained on normal traffic patterns. But, new highways open, drastically changing travel times.
Now, the model’s predictions are unreliable.
How to Detect and Fix Data Drift?
Detection Methods:
Feature Distribution Monitoring: Compare real-time input distributions with historical training data using statistical tests like Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) or Population Stability Index (PSI).
Drift Metrics: Track changes in mean, variance, and percentiles of key input features over-time.
Out-of-Distribution (OOD) Detection: Use anomaly detection models to flag inputs that differ significantly from training data.
Mitigation Strategies:
Frequent Model Retraining: Periodically update the model using the latest data.
Adaptive Models: Implement online learning techniques that allow models to adapt dynamically to new data distributions.
What is Concept Drift?
Unlike data drift, concept drift occurs when the relationship between features and the target changes.
Practically stating, what you’re trying to predict has changed.
Example
Say your cab fare model was trained on a per-mile pricing system. But stakeholders decided to switch to a flat-rate fare structure.
The input features remain the same, but their relationship to fare price has changed—making the model’s predictions inaccurate.
How to Detect and Fix Concept Drift
Detection Methods:
Feature-Target Relationship Analysis: Continuously track correlations between input variables (e.g., distance, time) and the target variable (fare price).
Error Distribution Monitoring: If prediction errors systematically increase over time, it may indicate concept drift.
Model Comparison: Maintain a simple baseline model; if its performance surpasses the production model, concept drift may be at play.
Mitigation Strategies:
Business Rule Awareness: Work closely with product teams to stay updated on evolving pricing policies.
Hybrid Approaches: Combine rule-based adjustments with ML models to accommodate dynamic pricing structures.
REMEMBER: To prevent silent model degradation, always question
has the data has changed?
has the business logic has shifted?
is the model is still aligned with reality?
By actively monitoring for data and concept drift, retraining models and collaborating with domain experts, you can stay ahead of model decay before it impacts business decisions.
Comment Down 👇: Have you ever faced model degradation? How did you handle it?
Until next time, happy learning!