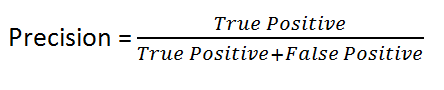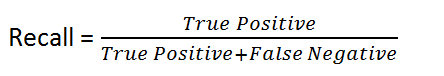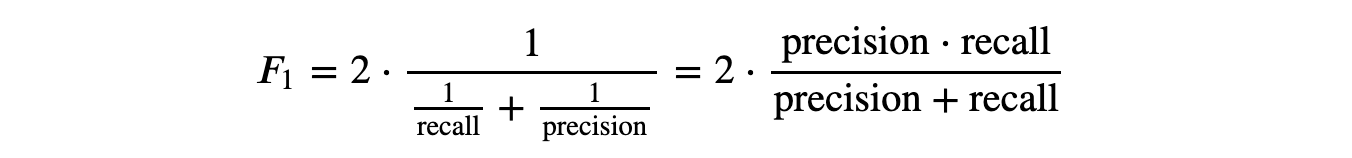Evaluation Metrics For Classification Models
What Every Data Scientist Should Know!
When evaluating the performance of a classification model like logistic regression, accuracy is usually the first metric that comes to minds of beginner data scientists.
It’s simple, intuitive and easy to compute.
But is it enough?
In many cases — especially when dealing with imbalanced data — accuracy alone can be misleading.
Let’s go through other reliable evaluation metrics in this read, in a simple and clear way.
If you’re new here Subscribe as here, I want to make Data Science easy for you. 👇🏻
What is Accuracy?
This metric that tells you how often the classifier model is correct.
You can calculate it as:
Accuracy = (Number of Correct Predictions) ÷ (Total number of Predictions
In Python, using accuracy_score, you can predict the accuracy of your model.
print(accuracy_score(test_target,y_pred)) # Output : 0.853This means the model was right 85.3% of the time.
But, When Accuracy Can Be Misleading?
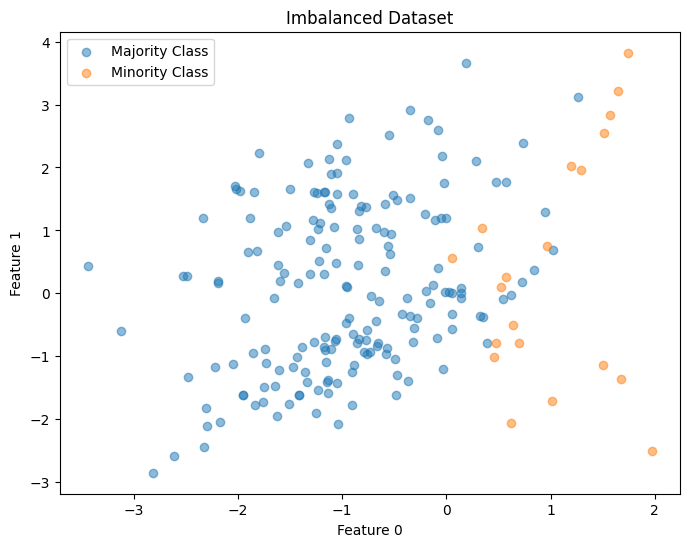
Accuracy fails when classes are imbalanced.
In cases where one class dominates the dataset, a classifier might achieve high accuracy by simply predicting the dominant class for all instances.
I’ve already covered a high-level overview of How to Handle Imbalanced Datasets. Missed it? (really?) Go check it out. 👇🏻
Handling Imbalanced Dataset in ML
·In this read, I want to focus on Imbalanced Datasets — a common challenge in real-world applications.
This is exactly why data scientists must know other evaluation metrics.
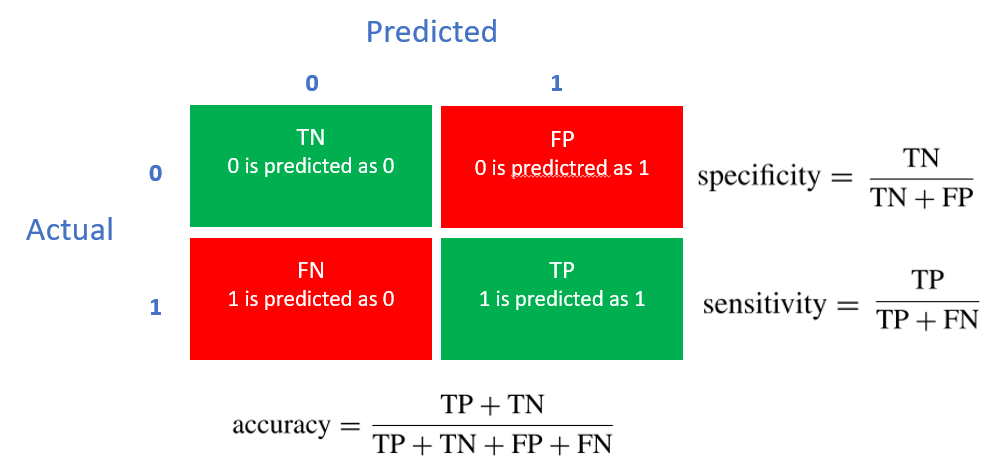
What is Confusion Matrix?
Simply stating, it's a table, that describes the performance of a classification model.
It presents a breakdown of the correct and incorrect predictions by each class.
Why Confusion Matrix Should Be Used?
As it provides more insights than accuracy alone.
It allows you to see where the model is making errors, such as confusing one class with another.
It’s also plays a vital role in designing effective A/B tests and accurately interpret the results.
In case you missed the Most Important Interview Question! Find it here: 👇🏻
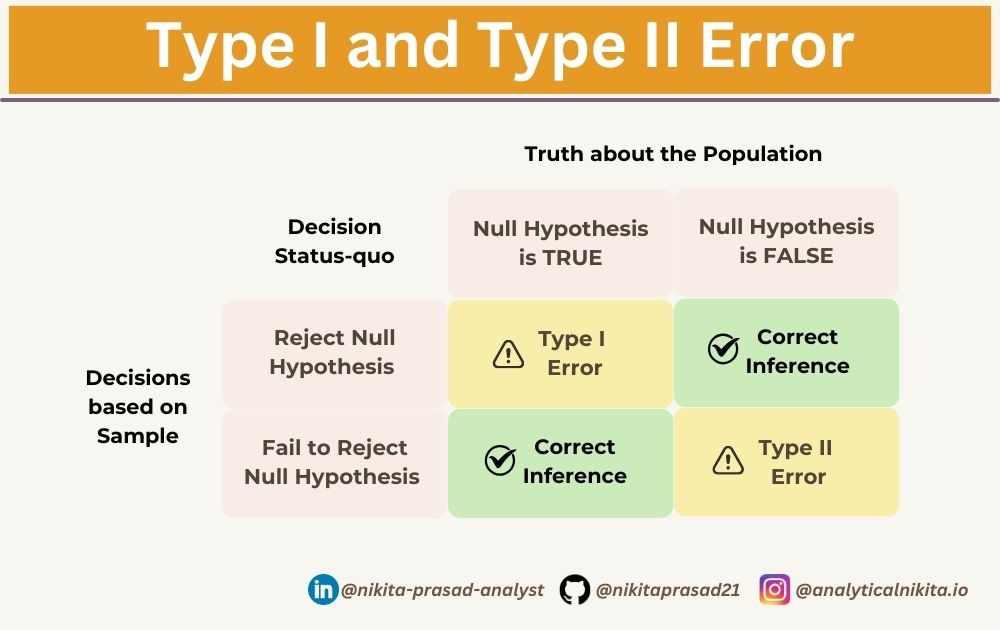
Understanding Type I and Type II Errors in Hypothesis Testing
·Without a solid understanding of statistics, it can be challenging to design effective A/B tests and accurately interpret the results.
So… Can You Calculate Accuracy from the Confusion Matrix?
Yes, you can.
You just have to sum up the correct predictions (True Positives and True Negatives) and divide by the total number of predictions.
where:
True Positives (TP): It is the case where you predicted Yes and the real output was also Yes.
True Negatives (TN): It is the case where you predicted No and the real output was also No.
False Positives (FP): It is the case where you predicted Yes but it was actually No.
False Negatives (FN): It is the case where you predicted No but it was actually Yes.
Note: But, the opposite is not possible. You cannot create a full Confusion Matrix just by knowing the Accuracy, because accuracy is just a number.
What is Precision?
It measures the accuracy of the positive predictions made by the classifier.
Here’s it’s formula:
Say, if the classifier predicts Yes 10 times, and only 7 were actually correct, then the precision is 7 out of 10, or 0.7.
What is Recall or Sensitivity?
Recall tells you how many actual positive cases your model was able to identify.
Here’s it’s formula:
Basically, it answers the question: “Out of all the real Yes cases, how many did the model find?”
Trade-Off between Precision & Recall
Often there’s a trade-off between precision and recall.
Meaning increasing one can decrease the other. Which one to prioritize depends on the application.
Many real-world applications requires a balance—this is where the F1 Scores comes in.
What is F1 Score?
F1 score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall.
It's useful when you want to find a balance between precision and recall, especially when classes are imbalanced.
Why Harmonic Mean?
Because it punishes extreme values more.
And, if either precision or recall is very low, the F1 Score will be low, helpful with imbalance classes.
What is Specificity?
While recall tell you how good the model is at identifying positives, specificity tells us how good it is at identifying negatives.
Useful in domains where detecting negatives correctly is just as important as positives.
Classification Report
Scikit-learn provides a classification report that summarizes all key metrics for each class, using the following code.
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))This typically includes:
Precision,
Recall,
F1 score,
Support (the number of actual samples for each class in the specified dataset).
If you’d like to explore the full implementation, including code and data, then checkout: Github Repository 👈🏻
Understanding these metrics helps data scientists make informed decisions about model performance, fairness, and suitability for real-world use.
Thanks for reading!
Until next time, happy learning!